010203
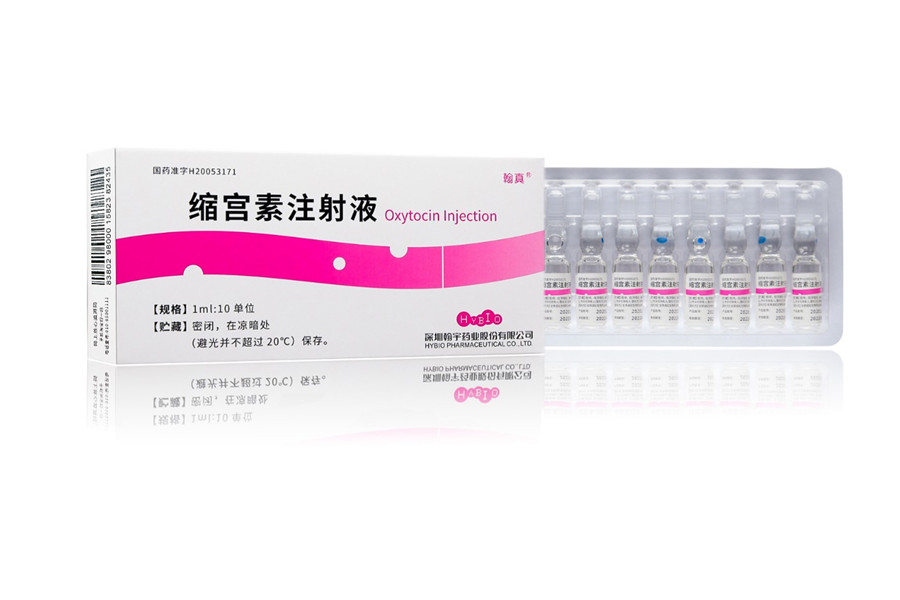
Oxytocin Injection
product description
Chemical Composition:
Oxytocin Injection is a synthetic form of oxytocin, a peptide hormone naturally produced by the pituitary gland. The synthetic version mimics the action of natural oxytocin by binding to oxytocin receptors on the uterine muscle, inducing contractions.
Mechanism of Action:
The primary mechanism by which oxytocin injection works is through the stimulation of uterine smooth muscle contractions. This action is critical for initiating labor in cases where it does not start naturally, enhancing labor when contractions are weak or ineffective, and controlling postpartum bleeding by contracting the uterus after delivery.
Indications and Usage:
Oxytocin Injection is indicated for the induction of labor in pregnant women with medical indications for the initiation of labor, such as preeclampsia or fetal distress. It is also used to augment labor in cases of stalled labor progress. Additionally, it is employed in the management of PPH, a leading cause of maternal mortality worldwide.
Administration and Dosage:
The administration of oxytocin injection can vary depending on its use. For labor induction or augmentation, it is typically administered intravenously, with the dosage carefully controlled to manage contraction intensity without compromising maternal or fetal safety. For PPH management, it may be administered intramuscularly or intravenously, depending on clinical circumstances and institutional protocols.
Efficacy and Outcomes:
Studies and clinical practice have demonstrated the efficacy of oxytocin injection in reducing the duration of labor and in the effective management of PPH. By promoting strong and regular uterine contractions, it helps in the delivery process and minimizes the risk of hemorrhage post-delivery.
Side Effects:
While generally safe, oxytocin injection can have side effects, including but not limited to, water intoxication due to its antidiuretic effects, uterine hyperstimulation which can compromise fetal oxygenation, and rare allergic reactions. Careful monitoring of the mother and fetus is essential during administration.
Contraindications and Precautions:
Oxytocin should not be used in certain situations, such as in women with significant cephalopelvic disproportion, unfavorable fetal positions that are undeliverable without surgical intervention, or in cases of severe fetal distress where immediate delivery is necessary. It is also contraindicated in women with hypersensitivity to oxytocin.